Cirrhosis
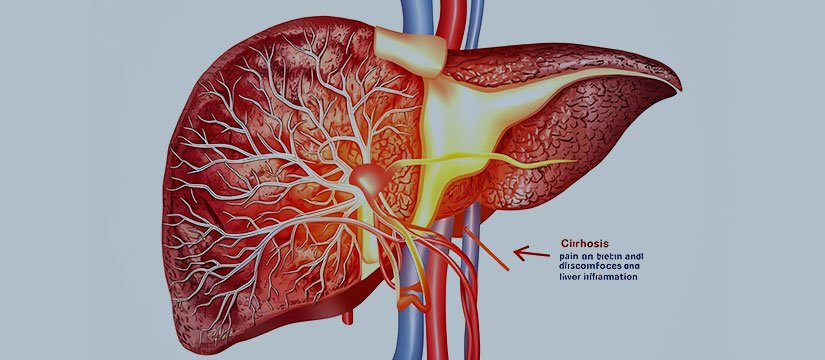
Cirrhosis – Condition Overview
Cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease in which healthy liver tissue is gradually replaced by scar tissue. This scarring interferes with normal liver function and can lead to liver failure.
The liver plays an essential role in digestion, detoxification, and metabolism. When cirrhosis develops, these vital processes become severely impaired.
Cirrhosis is usually irreversible, but early diagnosis and proper treatment can slow disease progression and prevent serious complications.
Symptoms of Cirrhosis
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- Yellowing of eyes and skin (Jaundice)
- Swelling of abdomen (Ascites)
- Swelling of legs and feet
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Blood in vomit or stools
- Confusion, sleep changes, or memory problems
Causes of Cirrhosis
- Chronic alcohol consumption
- Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C infection
- Fatty liver disease (NAFLD / NASH)
- Autoimmune liver diseases
- Bile duct disorders
- Genetic liver conditions
Complications of Cirrhosis
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Infections
- Hepatic encephalopathy
- Liver failure
- Increased risk of liver cancer
Treatment Options
- Complete avoidance of alcohol
- Balanced, liver-friendly diet
- Medications to manage complications
- Diuretics to reduce fluid buildup
- Endoscopic treatment for bleeding
- Liver transplant evaluation in advanced cases
Early diagnosis and continuous medical care can significantly improve survival and quality of life.
For expert consultation and treatment Contact us


